The term “New World Order” (NWO) gained prominence particularly after the end of the Cold War, symbolizing a shift in global power dynamics and the emergence of new geopolitical, economic, and social paradigms. The features of the New World Order encompass a broad range of elements that reflect the changing landscape of international relations and global governance. Here is a brief overview of its various features:
1. Unipolarity and US Dominance
– Global Hegemony: In the immediate aftermath of the Cold War, the United States emerged as the dominant global power, with significant military, economic, and cultural influence.
– Military Interventions: The US led various international interventions, such as in the Gulf War (1991) and later in Afghanistan (2001) and Iraq (2003), under the pretext of maintaining global stability and security.
2. Multilateralism and International Institutions
– United Nations (UN): The UN’s role in global governance was emphasized, with a focus on peacekeeping, conflict resolution, and promoting human rights.
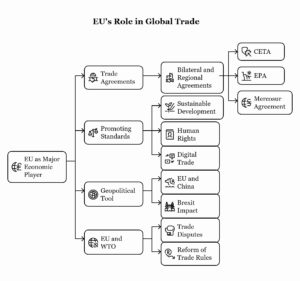
– International Organizations: Institutions like the World Trade Organization (WTO), International Monetary Fund (IMF), and World Bank played critical roles in economic governance and development.
3. Globalization
– Economic Integration: Increased interconnectedness of economies through trade liberalization, investment flows, and the proliferation of multinational corporations.
– Technological Advancements: Rapid advancements in technology and communication facilitated the global exchange of information, ideas, and culture.
4. Rise of Regional Powers
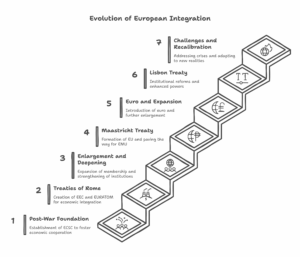
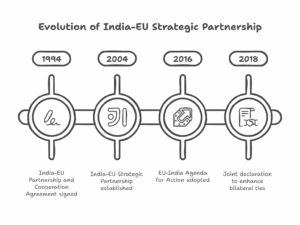
– Multipolarity: The emergence of regional powers such as China, the European Union, India, and Brazil, contributing to a more multipolar world order.
– Economic Blocks: Formation and strengthening of regional economic groupings like the European Union (EU), Association of Southeast Asian Nations (ASEAN), and MERCOSUR.
5. Economic Disparities and Development Challenges
– North-South Divide: Persistent economic disparities between developed (Global North) and developing (Global South) countries, highlighting issues of poverty, inequality, and underdevelopment.
– Sustainable Development: Emphasis on sustainable development goals (SDGs) to address global challenges such as poverty, health, education, and environmental sustainability.
6. Security Threats and Terrorism
– Non-State Actors: Rise of non-state actors and transnational terrorist organizations, such as Al-Qaeda and later ISIS, posing new security challenges.
– Asymmetric Warfare: Shift towards unconventional warfare and the need for new strategies to address global terrorism and cyber threats.
7. Human Rights and Democracy
– Democratization: Promotion of democratic governance and human rights as key components of international relations and development policies.
– Humanitarian Interventions: Increased focus on humanitarian interventions to prevent human rights abuses and genocides, often leading to debates on sovereignty and international law.
8. Environmental Concerns
– Climate Change: Growing recognition of climate change as a critical global issue, leading to international agreements such as the Kyoto Protocol (1997) and the Paris Agreement (2015).
– Sustainable Practices: Emphasis on adopting sustainable practices to protect the environment and ensure long-term ecological balance.
9. Global Health
– Pandemics: Recognition of global health threats, exemplified by the HIV/AIDS crisis and later the COVID-19 pandemic, highlighting the need for international cooperation in health.
Conclusion
The New World Order represents a complex and evolving framework of global governance characterized by US dominance, the rise of regional powers, economic globalization, and heightened focus on multilateralism, security, human rights, and environmental sustainability. While it offers opportunities for cooperation and development, it also poses challenges related to economic disparities, security threats, and the need for effective global governance mechanisms.

Leave a Reply