-
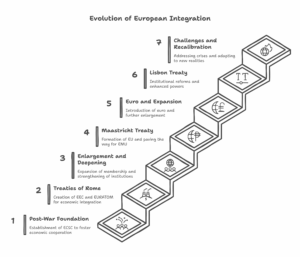 Continue reading →: Describe the major milestones in the integration of Europe.
Continue reading →: Describe the major milestones in the integration of Europe.The integration of Europe is one of the most ambitious and transformative political projects of the 20th and 21st centuries. It has evolved through several critical stages, shaped by historical events, economic needs, and political will. From the aftermath of World War II to the current European Union (EU), each…
-
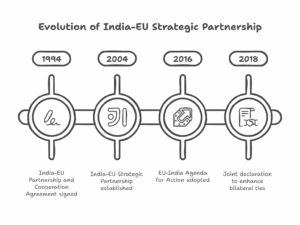 Continue reading →: Examine the nature of India-EU relations.
Continue reading →: Examine the nature of India-EU relations.India and the European Union (EU) share a long-standing and multifaceted relationship, characterized by cooperation in various domains such as trade, politics, security, development, science, technology, and people-to-people ties. As two large democracies with a shared commitment to multilateralism, democracy, and economic prosperity, their relations have evolved significantly over the…
-
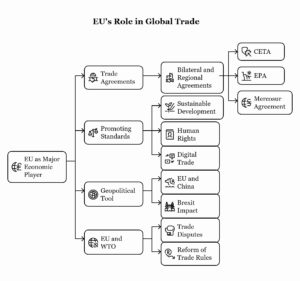 Continue reading →: What role is the European Union playing in the globalized trade?
Continue reading →: What role is the European Union playing in the globalized trade?The European Union (EU) is one of the world’s most influential economic entities and plays a significant role in shaping global trade. As a customs union and a single market, the EU has considerable economic weight, which it uses not only to influence trade policies within its borders but also…
-
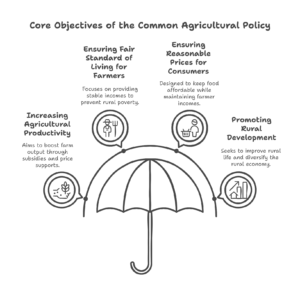 Continue reading →: Critically examine the common agricultural policy reforms in the European Union.
Continue reading →: Critically examine the common agricultural policy reforms in the European Union.The Common Agricultural Policy (CAP) of the European Union is one of the EU’s oldest and most important policies. Established in the 1960s, the CAP was designed to provide affordable food for EU citizens, ensure a stable income for farmers, and promote the development of rural areas across Europe. Over…
-
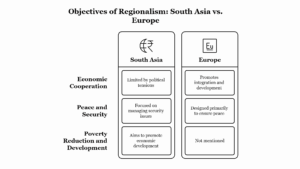 Continue reading →: “The objectives and processes of regionalism in Europe and South Asia differ considerably.”
Continue reading →: “The objectives and processes of regionalism in Europe and South Asia differ considerably.”Regionalism refers to the process through which countries in a particular region work together to achieve common objectives, typically aimed at enhancing economic, political, or security cooperation. While regionalism in Europe and South Asia both promote cooperation, the objectives, processes, and overall impact of regionalism in these two regions are…
-
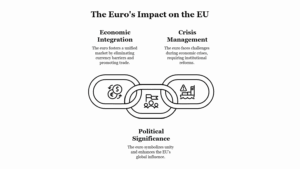 Continue reading →: Examine the importance and role of the Euro for the European Union and the World Economy.
Continue reading →: Examine the importance and role of the Euro for the European Union and the World Economy.The Euro (EUR), the official currency of the Eurozone—a monetary union of 19 out of the 27 European Union (EU) member states—has become one of the most important currencies globally, not only for the European Union but also in the broader context of the world economy. The adoption of the…
-
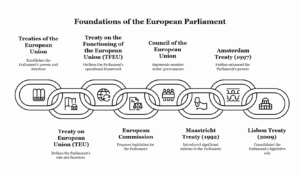 Continue reading →: Examine the constitution, role, and functions of the European Union Parliament.
Continue reading →: Examine the constitution, role, and functions of the European Union Parliament.The European Union (EU) Parliament, formally known as the European Parliament (EP), is one of the central institutions of the EU, playing a pivotal role in shaping EU legislation, scrutinizing the work of other EU institutions, and representing the interests of EU citizens. It is one of the few directly…
-
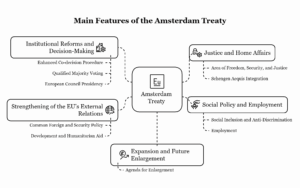 Continue reading →: Examine the main features of the Amsterdam Treaty
Continue reading →: Examine the main features of the Amsterdam TreatyThe Amsterdam Treaty, signed on October 2, 1997, and entered into force on May 1, 1999, represents a significant milestone in the evolution of the European Union (EU). It revised the Treaty on European Union (TEU) and the Treaty establishing the European Community (TEC), with the goal of enhancing the…
-
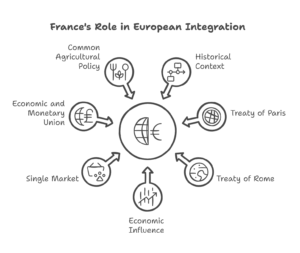 Continue reading →: Analyse the importance of France for the integration of Europe.
Continue reading →: Analyse the importance of France for the integration of Europe.France has been a pivotal actor in the process of European integration since the early stages of the European project. As one of the founding members of the European Economic Community (EEC), and later the European Union (EU), France’s political leadership, economic weight, and commitment to multilateralism have shaped the…
-
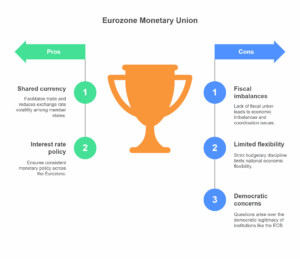 Continue reading →: Describe the background of the European Economic and Monetary Union.
Continue reading →: Describe the background of the European Economic and Monetary Union.The European Economic and Monetary Union (EMU) represents one of the most significant milestones in the European integration process. It aims to unify the economic and monetary policies of European Union (EU) member states through the adoption of a single currency and coordinated macroeconomic governance. The EMU is the culmination…
-
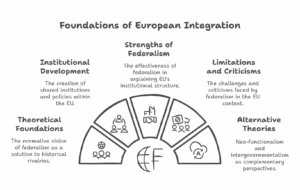 Continue reading →: Critically examine federalism as a theory to explain the process of European regional integration.
Continue reading →: Critically examine federalism as a theory to explain the process of European regional integration.Federalism, as a political theory and system, advocates for the division of powers between a central authority and constituent political units, typically aiming for shared governance while maintaining autonomy. In the context of European regional integration, federalism has played a foundational and ideological role, offering a framework for understanding the…
-
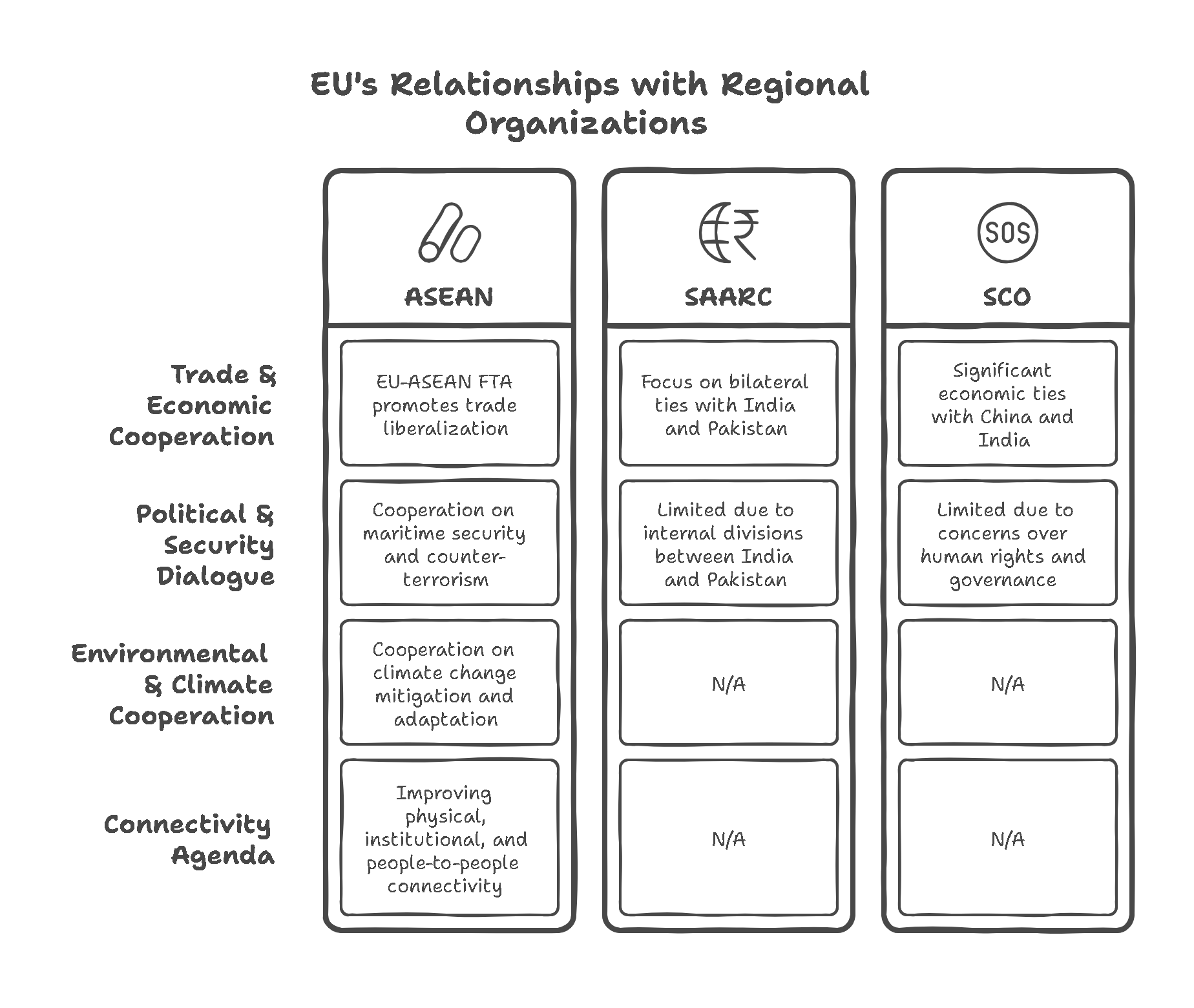 Continue reading →: Examine the nature of the European Union’s relationship with regional groupings in Asia.
Continue reading →: Examine the nature of the European Union’s relationship with regional groupings in Asia.The European Union (EU) has developed multifaceted and dynamic relationships with various regional groupings in Asia. These interactions are rooted in shared interests such as economic cooperation, regional stability, trade agreements, and environmental sustainability. However, the nature of the EU’s relationship with Asian regional groupings varies depending on historical contexts,…
WELCOME!
Yearly Archive
Categories List
- biodiversity
- Canada
- culture
- democracy
- economy
- European Union
- ignou
- india
- International Relations
- nature
- news
- political-philosophy
- political-science
- sustainability
- Uncategorized
- UPSC
Tag Cloud
agriculture ai business Canada china climate climate-change conservation diversity ethics european-union farming feminism finance gandhi health history ignou india KNOWLEDGE liberty mahatma-gandhi marxism nationalism nonviolence philosophy political-philosophy political-science political-theory politics poverty PSC religion renewable-energy russia socialism sociology sustainability sustainable-agriculture sustainable-living technology terrorism travel UPSC women
Term List
- africa
- agriculture
- ai
- aristotle
- bangladesh
- bjp
- business
- Canada
- china
- christianity
- climate
- climate-change
- conservation
- critical-theory
- digital-marketing
- diversity
- ecology
- elections
- ethics
- europe
- european-union
- faith
- farming
- fascism
- featured
- feminism
- feminist
- finance
- frankfurt-school
- freedom
- fundamentalism
- gandh
- gandhi
- gardening
- gender
- gender-equality
- global-warming
- government
- health
- herbs
- history
- human-rights
- ignou
- india
- inequality
- intellectual-property
- italy
- karl-marx
- KNOWLEDGE
- language
- law
- learning
- lenin
- liberty
- lifestyle
- linguistics
- mahatma-gandhi
- marx
- marxism
- mental-health
- MPS
- multicultural
- multiculturalism
- nationalism
- natural-remedies
- nonviolence
- organic-farming
- patents
- philosophy
- political-philosophy
- political-science
- political-theory
- politics
- pollution
- poverty
- PSC
- recycling
- religion
- renewable-energy
- russia
- socialism
- sociology
- soviet-union
- spirituality
- sustainability
- sustainable-agriculture
- sustainable-living
- teaching
- technology
- terrorism
- trademarks
- travel
- UPSC
- water
- water-conservation
- wellness
- wildlife
- women
- women-empowerment