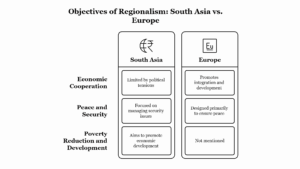
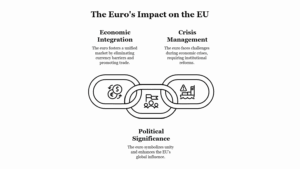
Multi-Dimensional Approach to Sustainable Development:
Sustainable development is inherently complex and interlinked, involving a variety of domains—economic, environmental, social, political, cultural, and technological. The multi-dimensional approach acknowledges that no single discipline or perspective is sufficient to capture the full scope of sustainability. Instead, it encourages an integrated, holistic framework that considers various sectors and stakeholders simultaneously.
Key Dimensions:
- Economic Dimension: Focuses on inclusive growth, employment, infrastructure, innovation, and resource efficiency.
- Environmental Dimension: Prioritizes natural resource conservation, ecosystem integrity, biodiversity, and pollution control.
- Social Dimension: Addresses equity, education, healthcare, gender equality, poverty alleviation, and cultural preservation.
- Political Dimension: Involves participatory governance, policy-making, justice, rule of law, and institutional integrity.
- Cultural and Ethical Dimension: Promotes respect for diverse values, traditional knowledge, and ethical responsibility toward nature.
- Technological Dimension: Emphasizes clean technologies, renewable energy, and digital innovations that align with sustainability goals.
Policy Orientation of the Multi-Dimensional Approach:
This approach influences public policy by promoting:
- Integrated Policy-Making: Connecting environmental and socio-economic planning to avoid fragmented development.
- Sustainability Indicators and Metrics: Using data-driven tools like HDI (Human Development Index), Ecological Footprint, and Environmental Performance Index (EPI) to monitor progress.
- Precautionary Principle: Advocating preventive action in the face of environmental uncertainty.
- Intergenerational Equity: Ensuring future generations inherit a livable planet.
- Participatory Governance: Including local communities, civil society, and indigenous people in decision-making.
- Resilience and Adaptation: Enhancing capacity to cope with climate change and disasters through adaptive policies.
Six Associated Approaches to Assess this Policy Orientation:
- Systems Thinking Approach: Considers the interdependence among various components of human and ecological systems.
- Capability Approach: Developed by Amartya Sen, this approach emphasizes people’s ability to lead the kind of life they value and have reason to value.
- Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA): Evaluates the consequences of development projects on ecosystems and biodiversity before execution.
- Life Cycle Assessment (LCA): Measures environmental impacts associated with all stages of a product’s life—from raw material extraction to disposal.
- Sustainable Livelihoods Approach (SLA): Focuses on people’s assets, capabilities, and activities required for a means of living.
- Triple Bottom Line (TBL): Encourages balancing profit (economic), people (social), and planet (environmental) in organizational goals and government policies.
These approaches enable a deeper understanding of sustainability trade-offs and synergies, leading to more balanced and long-term policy interventions.

Leave a Reply