Definition and Origin:
Sustainable development is a multifaceted concept that refers to a model of progress which meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. This widely accepted definition comes from the Brundtland Report (1987) titled Our Common Future, issued by the World Commission on Environment and Development (WCED).
The term emerged as a response to growing global concerns about unchecked economic growth, environmental degradation, depletion of natural resources, and social inequalities. It seeks to strike a balance among three core pillars:
- Economic Development
- Social Inclusion
- Environmental Protection
Each of these pillars is interdependent and essential to achieving a sustainable future.
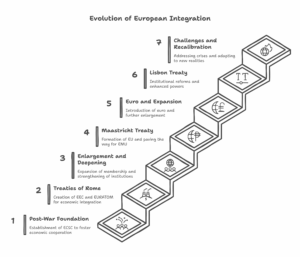
Historical Development:
- 1972 Stockholm Conference: First global summit on the environment.
- 1987 Brundtland Report: Introduced the term “sustainable development” into mainstream policy discourse.
- 1992 Earth Summit in Rio de Janeiro: Produced Agenda 21 and emphasized “local action” for sustainability.
- 2000 Millennium Development Goals (MDGs): Linked development with measurable goals.
- 2015 Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): Adopted by 193 countries, comprising 17 global goals to be achieved by 2030.
Core Principles of Sustainable Development:
- Intergenerational Equity: Future generations must inherit a planet that is not ecologically degraded.
- Intragenerational Equity: Social justice must be ensured among present populations; i.e., development must be inclusive.
- Precautionary Principle: If an action or policy may harm the environment or human health, precautionary steps must be taken even if some cause-and-effect relationships are not fully established scientifically.
- Polluter Pays Principle: Those who produce pollution should bear the costs of managing it.
- Participation and Good Governance: Inclusive, transparent, and accountable decision-making is vital.
Sustainable Development and India:
India, as a developing country with a large population and significant ecological challenges, has committed itself to the SDGs through its national development policies. Key initiatives such as the National Action Plan on Climate Change (NAPCC), Swachh Bharat Abhiyan, Smart Cities Mission, and Ujjwala Yojana reflect India’s attempt to align economic growth with sustainability goals.
Challenges to Achieving Sustainable Development:
- Poverty and Inequality: Marginalized groups often lack access to basic services.
- Overpopulation: Increased demand for natural resources.
- Pollution and Environmental Degradation: Air, water, and soil pollution continue to rise.
- Climate Change: Affects agriculture, water supply, and weather patterns.
- Unplanned Urbanization: Leads to slums, traffic congestion, and resource strain.
Academic Insight:
As Dr. Vandana Shiva, Indian environmentalist and author, explains:
“Development that displaces the poor and uproots ecosystems is not development, it is destruction.”
Vocabulary Tip:
- Equity (noun): fairness or justice in the way people are treated.
Inclusion (noun): the practice or policy of including people who might otherwise be excluded

Leave a Reply