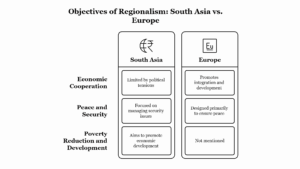
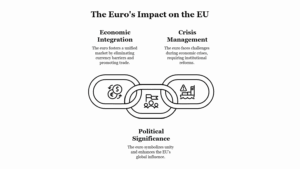
Political participation in India encompasses various forms of engagement by citizens in the political process, ranging from voting in elections to actively engaging in political activism and advocacy. Here’s a brief overview of political participation in India:
1. Electoral Participation:
– Voting in elections is the most common form of political participation in India. With its vibrant democracy, India conducts regular elections at the national, state, and local levels, attracting high voter turnout despite challenges such as logistical issues and voter apathy.
2. Political Activism:
– Political activism involves participating in protests, rallies, and demonstrations to advocate for social and political change. India has a long history of political activism, with movements led by civil society organizations, student groups, and political parties on various issues like corruption, social justice, and environmental protection.
3. Membership in Political Parties:
– Joining political parties allows citizens to actively engage in the political process by shaping party agendas, contesting elections, and influencing policy decisions. India has a multi-party system with numerous political parties representing diverse interests and ideologies.
4. Participation in Governance:
– Citizens can participate in governance processes through mechanisms like Gram Sabhas (village assemblies), Ward Committees, and Resident Welfare Associations (RWAs), where they can voice their concerns, participate in decision-making, and hold elected representatives accountable.
5. Social Media and Online Activism:
– With the proliferation of social media platforms, online activism has become increasingly prevalent in India. Citizens use social media to express their opinions, mobilize support for causes, and hold public officials accountable in real-time.
6. Volunteering and Community Engagement:
– Volunteering for political campaigns, community service projects, and grassroots initiatives allows citizens to contribute to their communities and participate in civic life.
7. Legal Advocacy and Public Interest Litigation (PIL):
– Legal advocacy and PILs provide avenues for citizens to seek justice and address social issues through the legal system. PILs have played a significant role in advancing human rights, environmental protection, and social justice in India.
Overall, political participation in India reflects the diversity and dynamism of its democratic process, with citizens engaging in a wide range of activities to express their political voice, influence policy decisions, and contribute to the development of the nation.

Leave a Reply