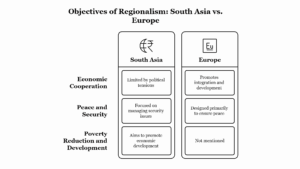
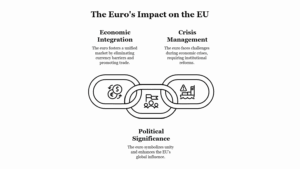
-
Continue reading →: Environmental Problems Associated with Sustainable Agriculture Practices
Sustainable agriculture aims to meet current food and textile needs without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs. While the intention is positive, certain environmental problems can still arise during the transition or implementation of sustainable practices. Key Environmental Problems: Conclusion: While sustainable agriculture aims to…
-
Continue reading →: Discuss the institutional mechanisms existing in the South Asian region for achieving sustainable development.
The South Asian region, comprising countries like India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Nepal, Bhutan, Sri Lanka, Maldives, and Afghanistan, faces a wide array of environmental, social, and economic challenges. These include rapid population growth, urbanization, poverty, natural disasters, and climate change. To address these challenges and promote sustainable development, several institutional mechanisms…
-
Continue reading →: Define sustainable livelihood as given by DFID. Describe in brief the five capitals from which individuals draw their livelihoods.
Sustainable livelihoods are a core component of sustainable development, especially in the context of poverty reduction, environmental management, and community resilience. The Department for International Development (DFID), UK, has developed a comprehensive Sustainable Livelihoods Framework (SLF) that is widely used to analyze and design poverty alleviation and development programs. Definition…
-
Continue reading →: Analyse the role of Civil Society Organizations in furthering environmental conservation in India.
Civil Society Organizations (CSOs)—including non-governmental organizations (NGOs), community-based groups, academic institutions, and environmental activists—play a pivotal role in India’s efforts to conserve its environment. Given the diversity and complexity of India’s environmental challenges, ranging from air and water pollution to deforestation and climate change, CSOs act as important agents of…
-
Continue reading →: What is cooperative marketing? List any four of its main functions.
Cooperative Marketing: Cooperative marketing refers to a system in which groups of producers (often farmers or artisans) come together to pool their resources and market their goods collectively. This collective approach enables them to have a stronger bargaining position, reduce costs, and access broader markets than they could individually. By…
-
Continue reading →: What is ethnoforestry? Explain and state ethano-silviculture refugia purposes served by it.
Ethnoforestry: Ethnoforestry is a branch of forestry that focuses on the relationship between indigenous and local communities and their surrounding forests. It involves the integration of traditional ecological knowledge with modern forestry practices to sustainably manage forest resources. Ethnoforestry recognizes that indigenous communities have a deep understanding of forest ecosystems…
-
Continue reading →: What are five M’s in the context of production technology? List any five benefits of an alternative manufacturing paradigm.
The Five M’s in production technology are essential components that contribute to the efficient and effective manufacturing process. These components help ensure that the production system operates smoothly and that resources are utilized optimally. Five Benefits of an Alternative Manufacturing Paradigm: An alternative manufacturing paradigm is a shift from conventional…
-
Continue reading →: Define traditional knowledge. List any four principles in building partnerships between scientific communities and traditional knowledge holders.
Definition of Traditional Knowledge: Traditional knowledge refers to the understanding, skills, practices, and innovations that are developed and accumulated by indigenous and local communities over generations. This knowledge is typically passed down orally and is closely linked to the cultural, environmental, and spiritual aspects of a community’s way of life.…
-
Continue reading →: Discuss the role of NGOs in protecting the environment.
Non-governmental organizations (NGOs) play a pivotal role in environmental protection at local, national, and global levels. Their functions range from grassroots mobilization to policy advocacy, making them critical players in the fight against environmental degradation. Below are the key roles played by NGOs: 1. Advocacy and Policy Influence NGOs often…
-
Continue reading →: Describe any five major challenges in taking global initiatives for environmental protection.
Global initiatives for environmental protection face numerous challenges, as environmental issues are complex and involve various stakeholders with different priorities. The following are five major challenges: 1. Lack of Political Will One of the most significant obstacles to effective global environmental protection is the lack of political will. Many countries…
-
Continue reading →: What is ESCAP? State any of its four main goals.
ESCAP stands for Economic and Social Commission for Asia and the Pacific, a regional arm of the United Nations established in 1947. ESCAP works with its 53 member states and 9 associate members to promote economic and social development in the Asia-Pacific region. Main Goals of ESCAP:
-
Continue reading →: What are the full forms of CPCB and SPCB? Describe their roles and responsibilities.
Full Forms: Roles and Responsibilities of CPCB: The Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB) is an autonomous organization under the Ministry of Environment, Forests, and Climate Change (MoEFCC) of the Government of India. It was constituted under the Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974, and later empowered under the…
WELCOME!
Yearly Archive
Categories List
- biodiversity
- Canada
- culture
- democracy
- economy
- European Union
- ignou
- india
- International Relations
- nature
- news
- political-philosophy
- political-science
- sustainability
- Uncategorized
- UPSC
Tag Cloud
agriculture ai business Canada china climate climate-change conservation diversity ethics european-union farming feminism finance gandhi health history ignou india KNOWLEDGE liberty mahatma-gandhi marxism nationalism nonviolence philosophy political-philosophy political-science political-theory politics poverty PSC religion renewable-energy russia socialism sociology sustainability sustainable-agriculture sustainable-living technology terrorism travel UPSC women
Term List
- africa
- agriculture
- ai
- aristotle
- bangladesh
- bjp
- business
- Canada
- china
- christianity
- climate
- climate-change
- conservation
- critical-theory
- digital-marketing
- diversity
- ecology
- elections
- ethics
- europe
- european-union
- faith
- farming
- fascism
- featured
- feminism
- feminist
- finance
- frankfurt-school
- freedom
- fundamentalism
- gandh
- gandhi
- gardening
- gender
- gender-equality
- global-warming
- government
- health
- herbs
- history
- human-rights
- ignou
- india
- inequality
- intellectual-property
- italy
- karl-marx
- KNOWLEDGE
- language
- law
- learning
- lenin
- liberty
- lifestyle
- linguistics
- mahatma-gandhi
- marx
- marxism
- mental-health
- MPS
- multicultural
- multiculturalism
- nationalism
- natural-remedies
- nonviolence
- organic-farming
- patents
- philosophy
- political-philosophy
- political-science
- political-theory
- politics
- pollution
- poverty
- PSC
- recycling
- religion
- renewable-energy
- russia
- socialism
- sociology
- soviet-union
- spirituality
- sustainability
- sustainable-agriculture
- sustainable-living
- teaching
- technology
- terrorism
- trademarks
- travel
- UPSC
- water
- water-conservation
- wellness
- wildlife
- women
- women-empowerment