-
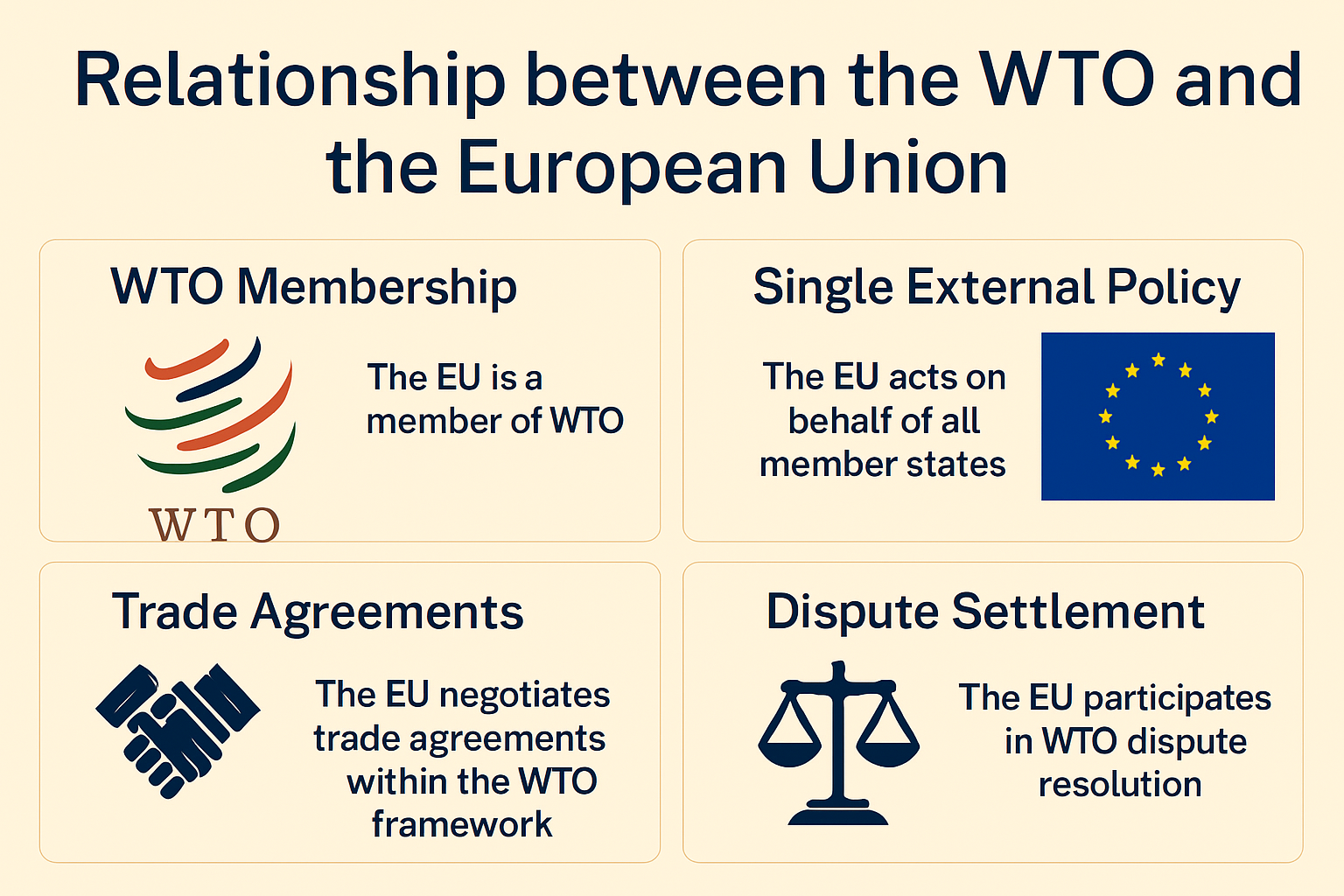 Continue reading →: Relationship between the WTO and the European Union
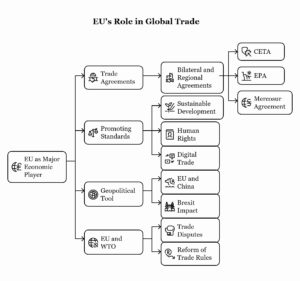
Continue reading →: Relationship between the WTO and the European UnionThe World Trade Organization (WTO) and the European Union (EU) share a complex and deeply interconnected relationship. As key players in global trade governance, both the WTO and the EU aim to promote free trade, fair competition, and the harmonization of trade rules across the world. While the WTO serves…
-
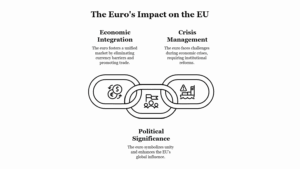
 Continue reading →: The Role of Germany in Strengthening the EU in View of Its Present Economic Position
Continue reading →: The Role of Germany in Strengthening the EU in View of Its Present Economic PositionGermany plays a crucial and central role in the European Union (EU) due to its economic strength, political influence, and strategic leadership within the EU framework. As the largest economy in Europe and the fourth-largest globally, Germany’s position within the EU is of great significance, especially in driving the EU’s…
-
Examine India’s Relations with the European Union
Published by
on
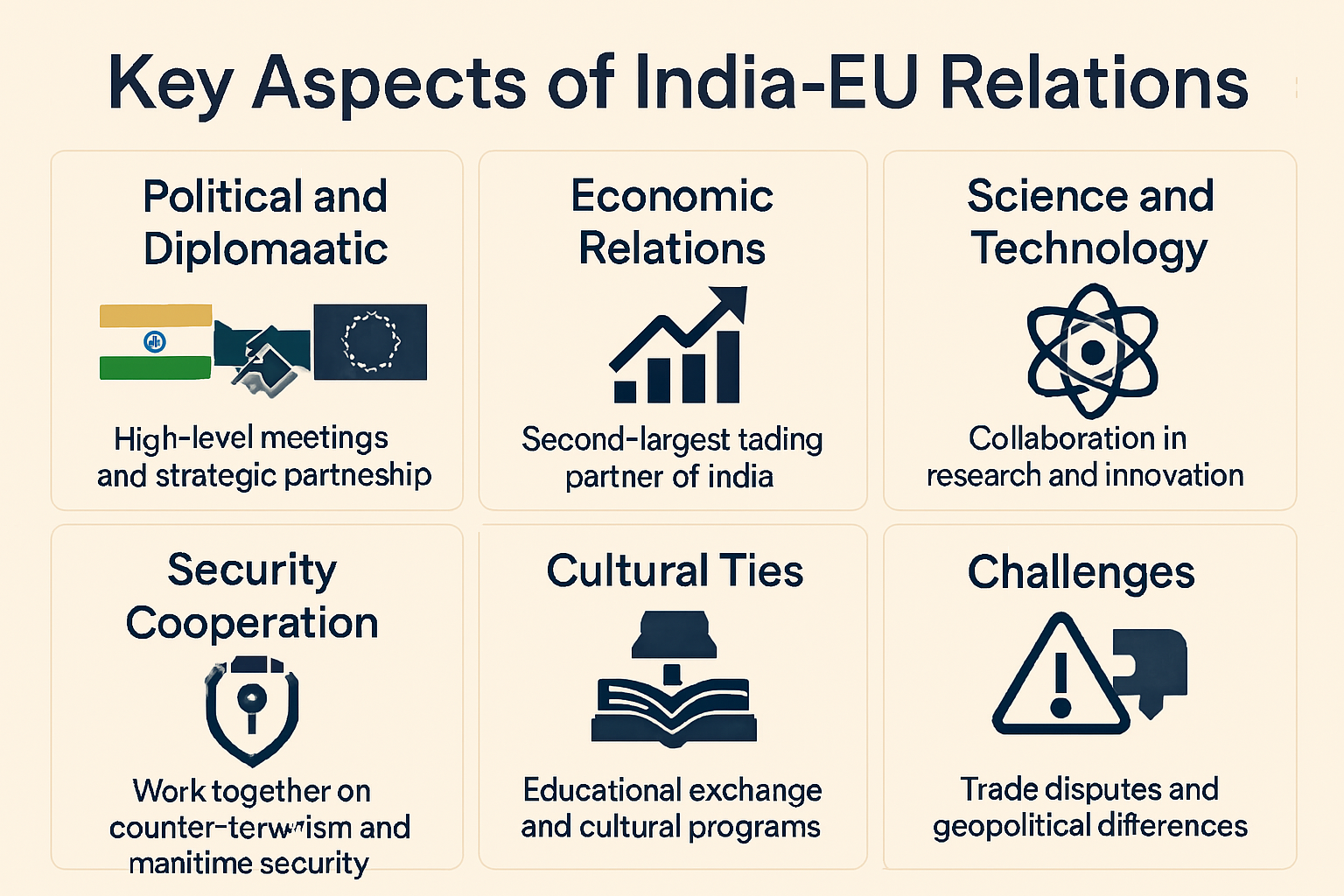 Continue reading →: Examine India’s Relations with the European Union
Continue reading →: Examine India’s Relations with the European UnionIndia’s relationship with the European Union (EU) is multifaceted, encompassing economic, political, strategic, and cultural ties. Since the establishment of formal diplomatic relations in 1963, India and the EU have strengthened their partnership, with both sides recognizing the importance of collaboration in addressing global challenges. The relationship has evolved significantly,…
-
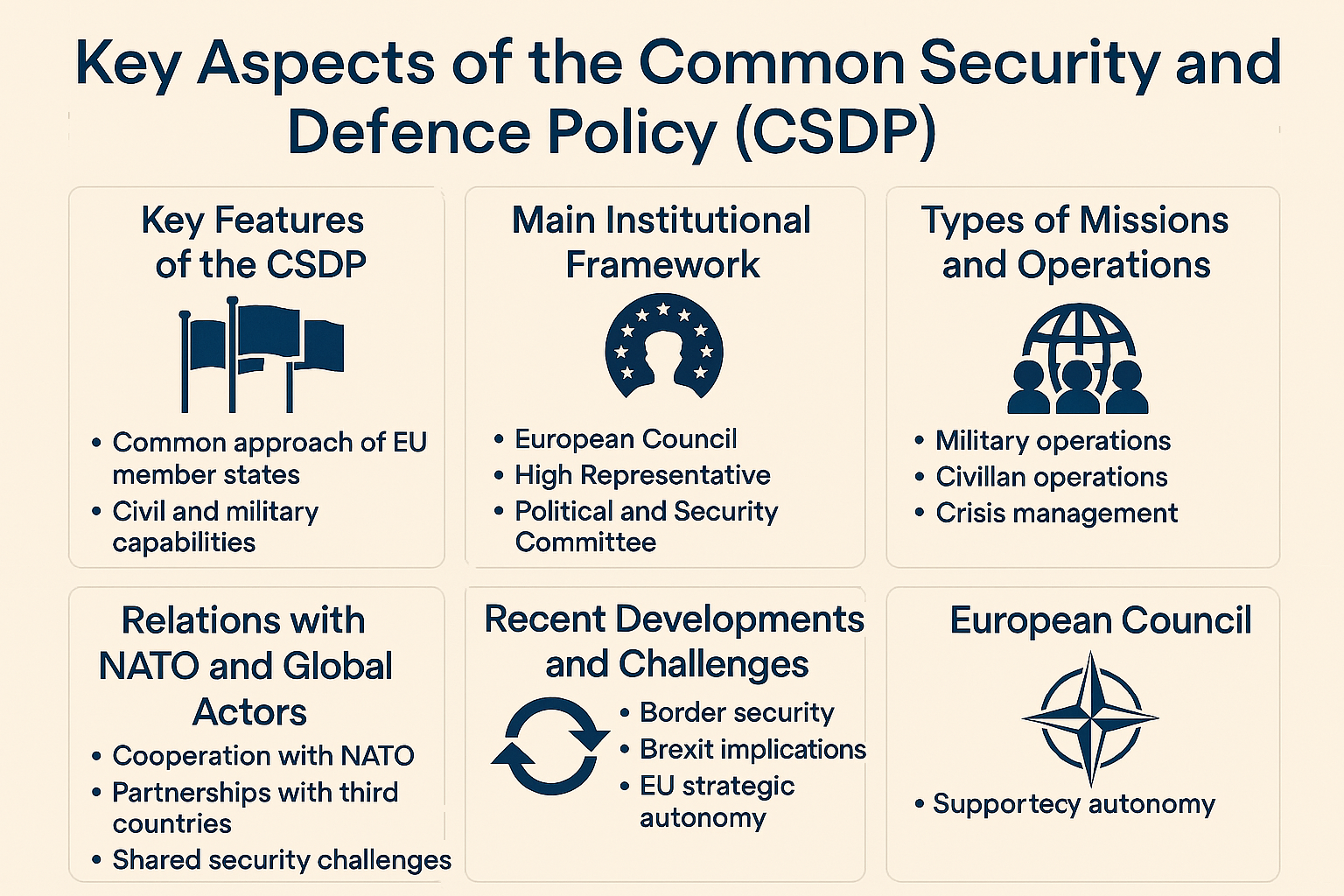 Continue reading →: Discuss the Common Security of the European Union
Continue reading →: Discuss the Common Security of the European UnionThe Common Security and Defence Policy (CSDP) is an integral part of the European Union’s (EU) overarching framework for foreign and security policy. It provides the EU with the means to address security challenges both within its borders and in the wider international environment. The CSDP aims to safeguard the…
-
 Continue reading →: Examine the Powers and Functions of the European Parliament
Continue reading →: Examine the Powers and Functions of the European ParliamentThe European Parliament (EP) is one of the most important and visible institutions within the European Union (EU). Established by the Treaty of Rome (1957), the EP has evolved significantly in terms of its powers, functions, and role in shaping EU policy. It is the only directly elected body in…
-
Evaluate the Main Tenets of Neo-functionalism
Published by
on
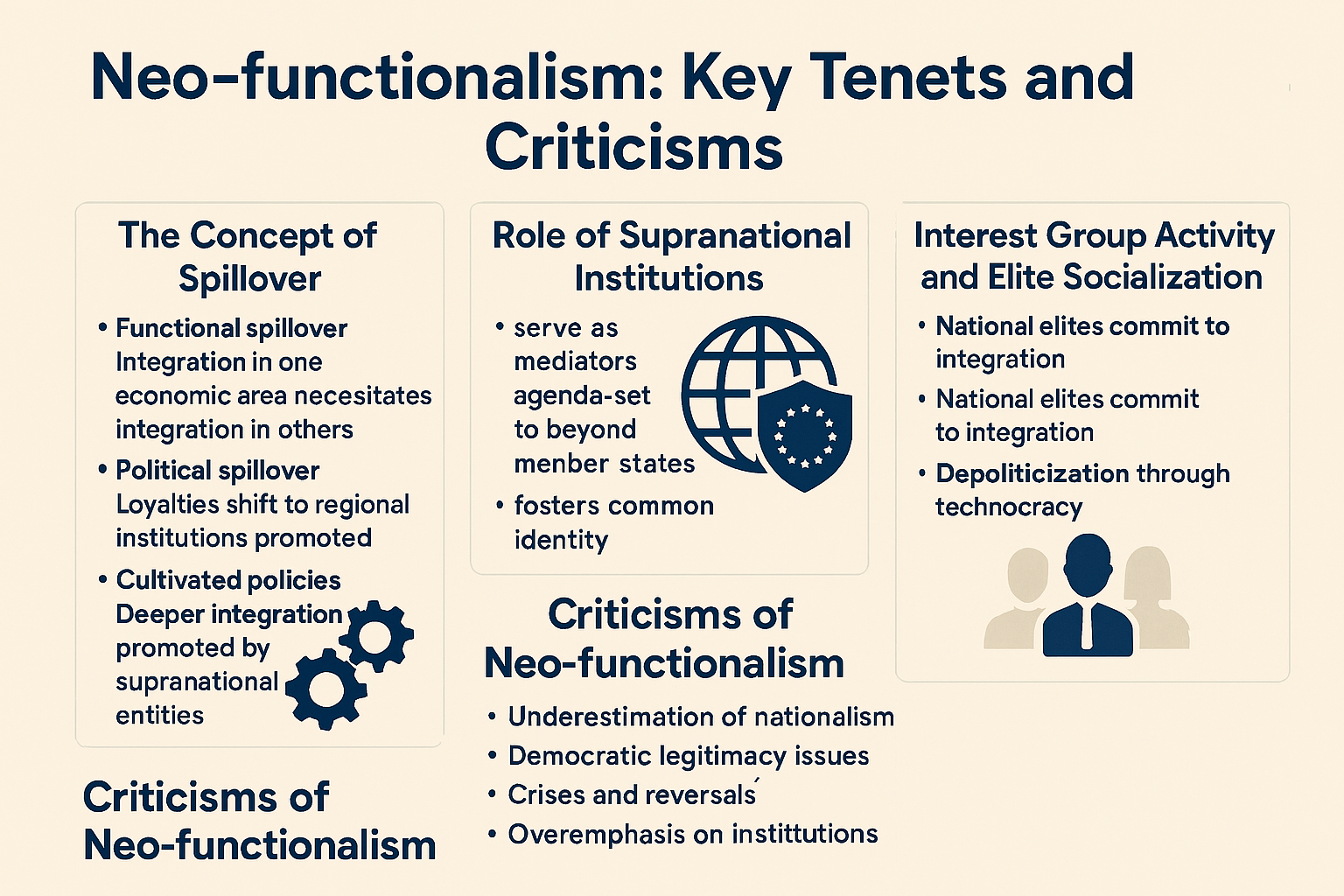 Continue reading →: Evaluate the Main Tenets of Neo-functionalism
Continue reading →: Evaluate the Main Tenets of Neo-functionalismNeo-functionalism is one of the foundational theoretical frameworks used to understand the process of regional integration, particularly in the context of post-World War II Europe. Developed in the mid-20th century, it offers insights into how and why sovereign states might choose to integrate in certain areas, ultimately leading to deeper…
-
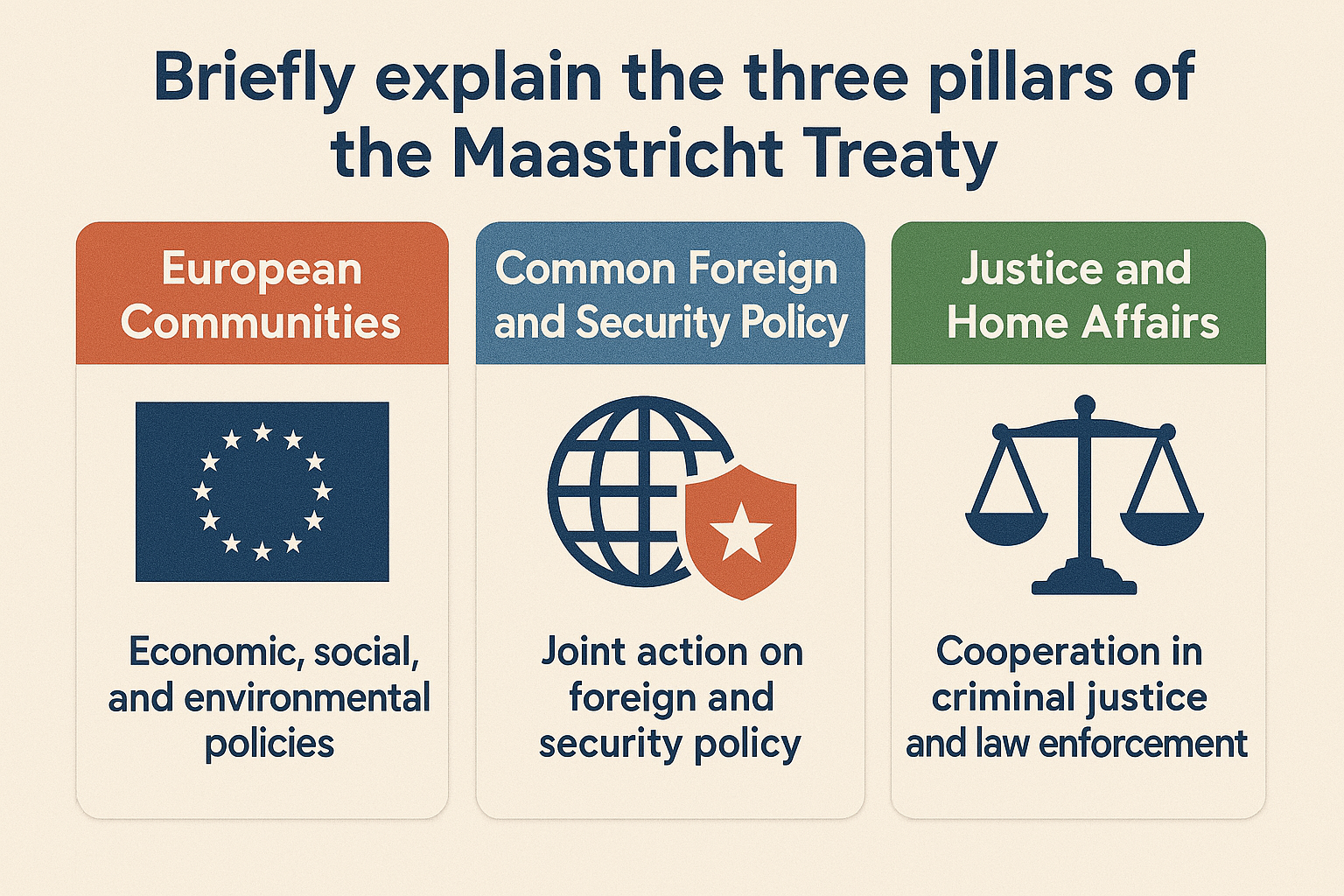 Continue reading →: Briefly explain the three pillars of the Maastricht Treaty
Continue reading →: Briefly explain the three pillars of the Maastricht TreatyThe Maastricht Treaty, formally known as the Treaty on European Union (TEU), was signed on 7 February 1992 and entered into force on 1 November 1993. It marked a significant evolution in the history of European integration by transforming the European Economic Community (EEC) into the European Union (EU) and…
-
 Continue reading →: Why should the ecosystem be conserved? Explain.
Continue reading →: Why should the ecosystem be conserved? Explain.Ecosystem conservation is vital for sustaining life on Earth, ensuring environmental stability, and supporting human well-being. An ecosystem comprises a dynamic community of living organisms (plants, animals, microorganisms) interacting with their physical environment (air, water, soil). These interactions form the basis of ecological balance, which, if disrupted, can lead to…
-
What is ADB? State any four of its goals.
Published by
on
 Continue reading →: What is ADB? State any four of its goals.
Continue reading →: What is ADB? State any four of its goals.The Asian Development Bank (ADB) is a regional multilateral development bank established in 1966 with the objective of fostering economic growth and cooperation among countries in the Asia-Pacific region. Headquartered in Manila, Philippines, ADB currently comprises 68 member countries, including both regional and non-regional members. The bank’s mission is to…
-
Continue reading →: Explain any two factors of inequality between developed and developing countries.
Inequality between developed and developing countries is a longstanding global issue that manifests in various dimensions, such as economic capacity, technological advancement, political influence, and environmental burden-sharing. Two key factors that significantly contribute to this inequality are technological disparity and historical patterns of colonization and resource exploitation. 1. Technological Disparity:…
-
 Continue reading →: Discuss the roadblocks to global initiatives for environmental protection
Continue reading →: Discuss the roadblocks to global initiatives for environmental protectionGlobal environmental protection efforts have gained considerable momentum since the 1972 Stockholm Conference, culminating in landmark initiatives such as the Rio Earth Summit (1992), the Kyoto Protocol (1997), the Paris Agreement (2015), and the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). However, despite decades of international negotiations and frameworks, meaningful and coordinated global…
-
 Continue reading →: Role of Cooperatives in Sustainable Development
Continue reading →: Role of Cooperatives in Sustainable DevelopmentCooperatives play a pivotal role in advancing sustainable development by combining economic goals with social responsibility and environmental stewardship. A cooperative is a voluntary association of individuals united to meet common economic, social, and cultural needs through a jointly owned and democratically controlled enterprise. Rooted in principles of mutual help,…
WELCOME!
Yearly Archive
Categories List
- biodiversity
- Canada
- culture
- democracy
- economy
- European Union
- ignou
- india
- International Relations
- nature
- news
- political-philosophy
- political-science
- sustainability
- Uncategorized
- UPSC
Tag Cloud
agriculture ai business Canada china climate climate-change conservation diversity ethics european-union farming feminism finance gandhi health history ignou india KNOWLEDGE liberty mahatma-gandhi marxism nationalism nonviolence philosophy political-philosophy political-science political-theory politics poverty PSC religion renewable-energy russia socialism sociology sustainability sustainable-agriculture sustainable-living technology terrorism travel UPSC women
Term List
- africa
- agriculture
- ai
- aristotle
- bangladesh
- bjp
- business
- Canada
- china
- christianity
- climate
- climate-change
- conservation
- critical-theory
- digital-marketing
- diversity
- ecology
- elections
- ethics
- europe
- european-union
- faith
- farming
- fascism
- featured
- feminism
- feminist
- finance
- frankfurt-school
- freedom
- fundamentalism
- gandh
- gandhi
- gardening
- gender
- gender-equality
- global-warming
- government
- health
- herbs
- history
- human-rights
- ignou
- india
- inequality
- intellectual-property
- italy
- karl-marx
- KNOWLEDGE
- language
- law
- learning
- lenin
- liberty
- lifestyle
- linguistics
- mahatma-gandhi
- marx
- marxism
- mental-health
- MPS
- multicultural
- multiculturalism
- nationalism
- natural-remedies
- nonviolence
- organic-farming
- patents
- philosophy
- political-philosophy
- political-science
- political-theory
- politics
- pollution
- poverty
- PSC
- recycling
- religion
- renewable-energy
- russia
- socialism
- sociology
- soviet-union
- spirituality
- sustainability
- sustainable-agriculture
- sustainable-living
- teaching
- technology
- terrorism
- trademarks
- travel
- UPSC
- water
- water-conservation
- wellness
- wildlife
- women
- women-empowerment