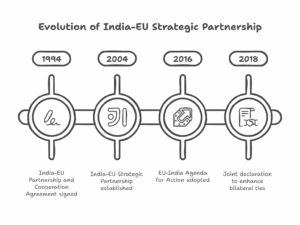
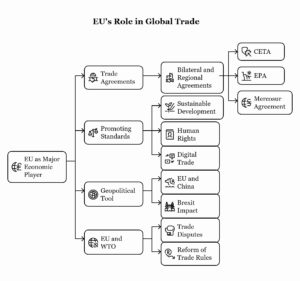
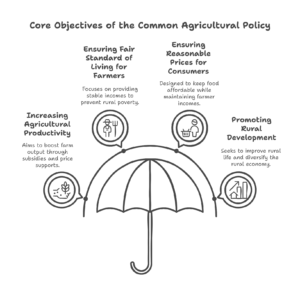
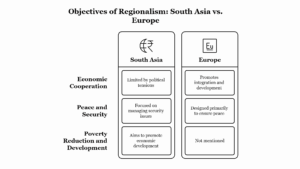
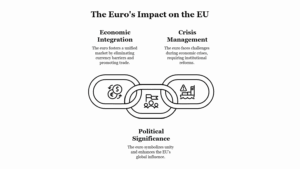
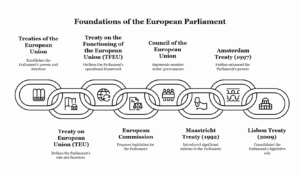
-
Continue reading →: Development as Freedom
The concept of “Development as Freedom” was introduced by Amartya Sen in his influential book, Development as Freedom (1999). Sen argues that the true measure of development should not be confined to economic growth alone, but should encompass the freedom and capabilities that enable individuals to lead a life they…
-
Continue reading →: Nature of Inter-State Disputes in India
Inter-state disputes in India are an inherent part of the country’s federal structure. Given the diversity in language, culture, religion, geography, and economic development, conflicts often arise between states over various issues, including territorial boundaries, water-sharing, governance, and resources. The political landscape of India is shaped by these disputes, which…
-
Continue reading →: The impact of globalisation on State politics in India
Globalisation, broadly defined as the increased interconnectedness and interdependence of economies, societies, and cultures through trade, communication, and technology, has had far-reaching consequences on the political, economic, and social fabric of India. Since the economic liberalisation of 1991, India has embraced globalisation through the opening up of markets, deregulation, and…
-
Continue reading →: Linguistic Minorities and Politics
Linguistic minorities in India face unique challenges in terms of political representation, cultural preservation, and social integration. India’s diversity is reflected not only in its ethnic and religious composition but also in its linguistic variety. The Constitution of India recognizes 22 official languages under the Eighth Schedule, and there are…
-
Continue reading →: Politics of Water Disputes Between States
Water disputes between states in India are a significant issue in the country’s federal system. India, being a largely agrarian economy, relies heavily on water resources for agriculture, industry, and drinking purposes. The mismanagement and unequal distribution of water resources have given rise to frequent conflicts between states. The politics…
-
Continue reading →: The problem of insurgency is related to the issues of development, inter-ethnic relations, and autonomy
Insurgency in India has been a persistent issue, particularly in certain regions, and it is deeply intertwined with issues related to development, inter-ethnic relations, and autonomy. These issues form the core of the grievances that fuel insurgent movements, as marginalized groups and regions seek justice, recognition, and the fulfillment of…
-
Continue reading →: Nature of Self-Determination Movements in India
Self-determination movements in India are primarily concerned with the demand for greater autonomy or even independence, based on identity, ethnicity, language, or historical grievances. These movements are often fueled by a sense of alienation from the central government, which some groups feel fails to address their specific cultural, economic, or…
-
Continue reading →: Constitutional Mechanisms to Resolve Inter-State Disputes
Inter-state disputes in India, whether over water, land, boundaries, or other resources, have been a recurring issue. The Indian Constitution provides various mechanisms for resolving these disputes, primarily to maintain harmony between the federal and state governments. The key constitutional mechanisms include: In summary, the Indian Constitution provides a range…
-
Continue reading →: Factors leading to the fragmentation of party system in India
The fragmentation of the party system in India is a significant development in the country’s political landscape. Over time, the once relatively unified party system, dominated by the Indian National Congress (INC), has given way to a more complex and fragmented political structure. This fragmentation has been a result of…
-
Continue reading →: Examine the State policies that have contributed to agrarian transformation in India
Agrarian transformation in India has been a result of several state policies that have aimed at modernizing agriculture, improving productivity, and addressing the socio-economic conditions of the rural population. These policies have evolved over time, responding to the changing demands of food security, economic development, and social justice. State interventions…
-
Continue reading →: Briefly describe the systemic and post-modernist frameworks to analyse State politics in India
In the study of state politics in India, two significant theoretical frameworks are the systemic and post-modernist approaches. Both offer distinct perspectives on how the state operates, the nature of political power, and the dynamics of governance in India. These frameworks help scholars and analysts understand the political landscape of…
-
Continue reading →: The factors contributing to the breakdown of the Congress system
The Congress system in India, often referred to as the “Congress dominance” or the “Congress system of politics,” refers to the period between 1947 and the early 1970s when the Indian National Congress (INC) was the dominant political party in India. The Congress party played a central role in India’s…
WELCOME!
Yearly Archive
Categories List
- biodiversity
- Canada
- culture
- democracy
- economy
- European Union
- ignou
- india
- International Relations
- nature
- news
- political-philosophy
- political-science
- sustainability
- Uncategorized
- UPSC
Tag Cloud
agriculture ai business Canada china climate climate-change conservation diversity ethics european-union farming feminism finance gandhi health history ignou india KNOWLEDGE liberty mahatma-gandhi marxism nationalism nonviolence philosophy political-philosophy political-science political-theory politics poverty PSC religion renewable-energy russia socialism sociology sustainability sustainable-agriculture sustainable-living technology terrorism travel UPSC women
Term List
- africa
- agriculture
- ai
- aristotle
- bangladesh
- bjp
- business
- Canada
- china
- christianity
- climate
- climate-change
- conservation
- critical-theory
- digital-marketing
- diversity
- ecology
- elections
- ethics
- europe
- european-union
- faith
- farming
- fascism
- featured
- feminism
- feminist
- finance
- frankfurt-school
- freedom
- fundamentalism
- gandh
- gandhi
- gardening
- gender
- gender-equality
- global-warming
- government
- health
- herbs
- history
- human-rights
- ignou
- india
- inequality
- intellectual-property
- italy
- karl-marx
- KNOWLEDGE
- language
- law
- learning
- lenin
- liberty
- lifestyle
- linguistics
- mahatma-gandhi
- marx
- marxism
- mental-health
- MPS
- multicultural
- multiculturalism
- nationalism
- natural-remedies
- nonviolence
- organic-farming
- patents
- philosophy
- political-philosophy
- political-science
- political-theory
- politics
- pollution
- poverty
- PSC
- recycling
- religion
- renewable-energy
- russia
- socialism
- sociology
- soviet-union
- spirituality
- sustainability
- sustainable-agriculture
- sustainable-living
- teaching
- technology
- terrorism
- trademarks
- travel
- UPSC
- water
- water-conservation
- wellness
- wildlife
- women
- women-empowerment