The India-European Union (EU) Strategic Partnership represents a significant dimension of India’s foreign policy, characterized by political, economic, and cultural cooperation between two major global actors. The partnership, officially established in 2004, has evolved into one of the most comprehensive relationships between India and any international organization. The relationship is underpinned by shared interests in global stability, peace, and prosperity, as well as a common commitment to democratic values, sustainable development, and multilateralism.
1. Background of the Partnership
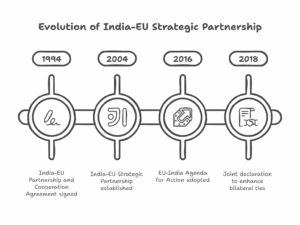
India and the EU share a long history of cooperation, with formal diplomatic relations dating back to the 1960s. However, the formalization of their strategic partnership in 2004 marked a new phase, signaling both sides’ recognition of the growing importance of each other in a rapidly changing global landscape. The partnership, thus, was not just a response to current global challenges but also a recognition of the evolving international order in the 21st century. This partnership, driven by mutual respect and shared values, was built on three key pillars:
- Political Dialogue
- Economic and Trade Relations
- People-to-People and Cultural Links
2. Key Areas of Cooperation
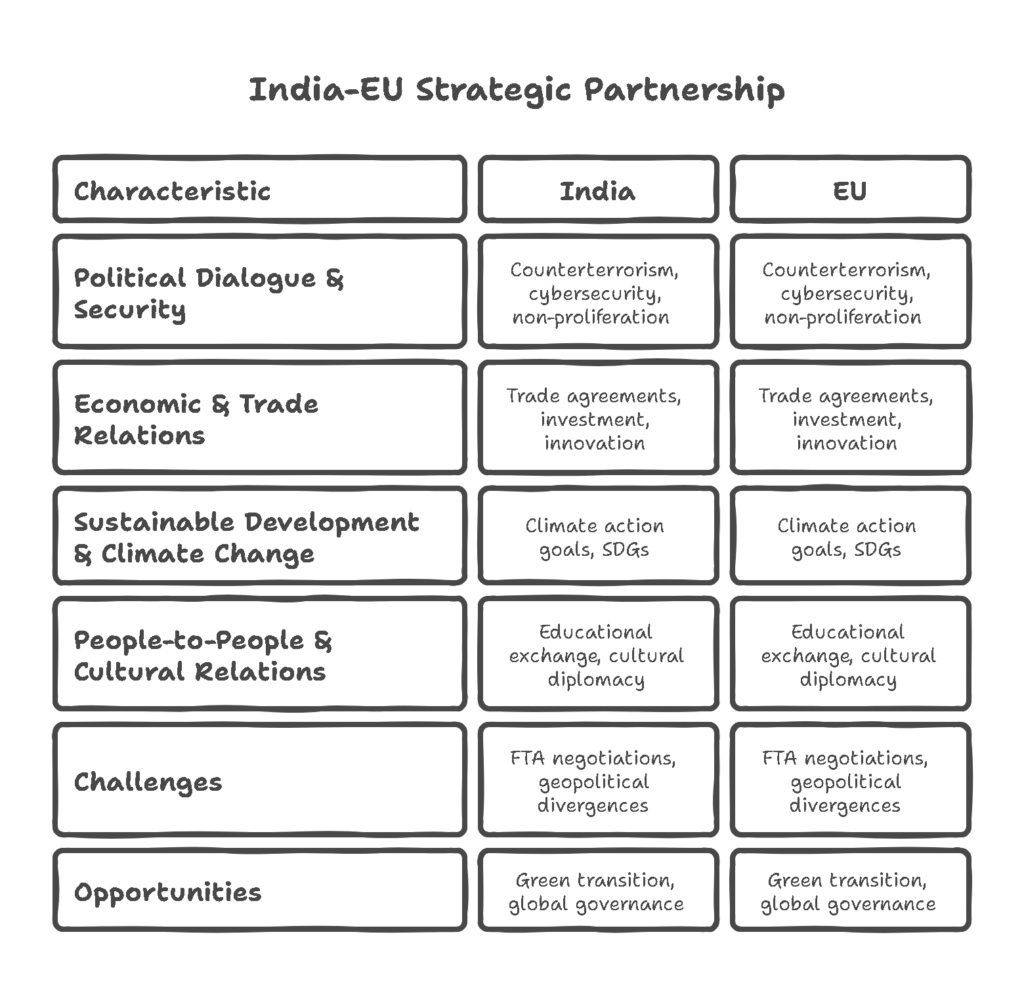
2.1 Political Dialogue and Security Cooperation
The political dialogue between India and the EU is focused on strengthening bilateral relations, addressing regional and global security concerns, and advancing peace and stability. The EU and India have cooperated closely on issues such as counterterrorism, cybersecurity, and non-proliferation. This cooperation is critical given the volatile security environment in South Asia and the EU’s own security concerns related to terrorism and conflicts in its neighboring regions.
- Counterterrorism Cooperation: Both India and the EU have recognized the threat posed by terrorism and have collaborated on various initiatives to address it, including information sharing, strengthening counterterrorism measures, and combating extremism.
- Regional Stability: India and the EU also engage in discussions on promoting peace and stability in regions such as Afghanistan, the Middle East, and Africa. The EU has supported India’s efforts in regional diplomacy, particularly in fostering dialogue and cooperation in South Asia.
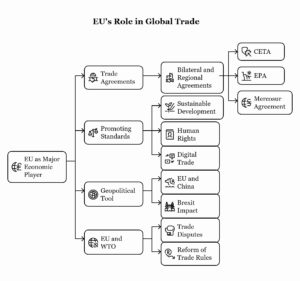
2.2 Economic and Trade Relations
The economic and trade dimensions of the India-EU strategic partnership are vital to both parties, as they represent significant economic players globally. The EU is India’s largest trading partner, and India is the EU’s 9th largest trading partner. Trade and investment are the backbone of this relationship, and efforts to enhance economic cooperation have been ongoing.
- Trade Agreements: The India-EU Free Trade Agreement (FTA) has been a long-standing objective, aimed at improving market access and reducing trade barriers between the two entities. Although negotiations for the FTA have faced several challenges, including differences over issues such as market access, intellectual property, and data protection, there is still strong political will to finalize it. In the meantime, India and the EU have worked on bilateral trade agreements in areas like goods, services, and investment.
- Investment and Innovation: The EU is one of the largest foreign investors in India, particularly in sectors such as manufacturing, information technology, and renewable energy. Both sides have also explored collaboration in research and innovation, including partnerships in technology transfer, renewable energy, and climate change mitigation.
2.3 Sustainable Development and Climate Change
One of the major areas of cooperation between India and the EU is in the realm of sustainable development and climate change. Both India and the EU face significant challenges in addressing climate change, and they have been active participants in global environmental forums such as the Paris Agreement.
- Climate Change Mitigation: The EU has been a strong supporter of India’s climate action goals, providing technical and financial support for India’s transition to a low-carbon economy. This includes collaboration on renewable energy projects, such as solar power, where India has ambitious targets to become a global leader.
- Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): India and the EU also work together towards the achievement of the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Through cooperation on water management, agriculture, clean energy, and health, both sides aim to address shared global challenges.
2.4 People-to-People and Cultural Relations
Cultural and people-to-people ties have been a fundamental aspect of the India-EU partnership, fostering mutual understanding and deepening connections between the peoples of both regions.
- Educational Exchange: India and the EU have established programs for academic exchanges, joint research, and student mobility. The EU’s Erasmus Mundus program, for instance, facilitates the exchange of students and scholars between India and European universities.
- Cultural Diplomacy: The EU’s support for Indian cultural initiatives, including art exhibitions, theater performances, and film festivals, has strengthened the cultural ties between the two entities. These exchanges not only promote the rich cultural heritage of India but also encourage deeper understanding and respect for cultural diversity.
3. Challenges and Opportunities
Despite the deepening of India-EU relations, the partnership faces several challenges:
- Trade Negotiations: The long-standing negotiations over the FTA have yet to yield a concrete agreement, largely due to differences over trade-related issues such as market access, intellectual property protection, and data privacy.
- Geopolitical Divergences: There are some divergences in terms of geopolitical priorities. India’s strategic alignment with countries such as the United States and Russia, as well as its growing engagement with regional groupings like BRICS and SCO, sometimes differs from the EU’s strategic priorities, particularly in terms of global governance and security issues.
Nevertheless, the opportunities for growth are substantial:
- Green Transition: The EU’s commitment to a Green New Deal and India’s ambition to lead in renewable energy provide significant opportunities for cooperation in clean technologies, energy transition, and climate policy.
- Global Governance: Both India and the EU share a commitment to strengthening multilateralism, making cooperation in global forums like the United Nations, World Trade Organization (WTO), and G20 crucial. Their shared interests in reforming global institutions and strengthening the rules-based international order can provide a foundation for deeper cooperation.
4. Conclusion
The India-EU Strategic Partnership is an essential framework that has allowed both sides to foster cooperation across multiple sectors, from political and security cooperation to trade, investment, and cultural exchange. While there are challenges in finalizing the Free Trade Agreement and aligning geopolitical priorities, the partnership’s potential for growth and collaboration in areas such as sustainable development, climate change, and innovation remains significant. Both sides are committed to deepening their ties, recognizing the need for a multilateral approach to address global challenges and promote peace, prosperity, and stability.

Leave a Reply