In India, environmental protection laws, particularly those related to air and water pollution, are aimed at preventing and controlling the degradation of natural resources. These laws have evolved over time in response to growing concerns about the detrimental impact of industrialization and urbanization on the environment.
Air Pollution Legislation:
- The Air (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1981: This Act empowers the central and state pollution control boards to establish standards for air quality and to regulate emissions from industries and vehicles. It provides mechanisms for the control of air pollution, including the establishment of air quality monitoring stations and penalties for violators.
- National Air Quality Standards (NAAQS): These standards, issued by the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB), set permissible levels of pollutants such as sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, particulate matter, carbon monoxide, and ozone.
- The Motor Vehicles Act (1989): This Act includes provisions to regulate vehicular emissions, particularly in urban areas. It mandates the use of cleaner fuels and introduces measures for the inspection and maintenance of vehicle emissions.
Water Pollution Legislation:
- The Water (Prevention and Control of Pollution) Act, 1974: This law was enacted to prevent and control water pollution by establishing the Central and State Pollution Control Boards. It sets standards for the discharge of effluents into water bodies and mandates industries to obtain consent before discharging wastewater.
- National Water Quality Standards (NWQS): These standards, established by the CPCB, define permissible levels of pollutants in water bodies. They aim to protect public health and aquatic ecosystems.
- The Environment Protection Act, 1986: Although not specifically focused on air or water pollution, this Act provides a framework for the protection of the environment. It allows the government to take measures to control and prevent environmental pollution, including air and water pollution.

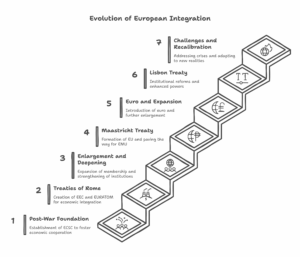
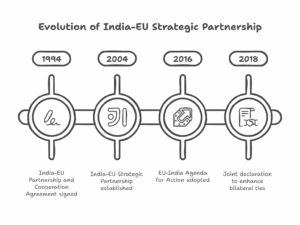
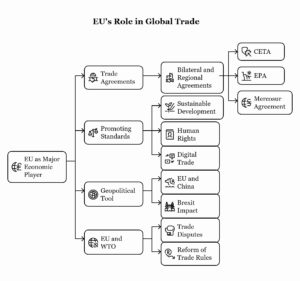
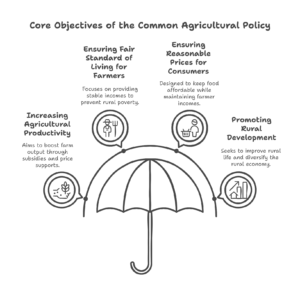
Leave a Reply