Theories of nationalism seek to explain the origins, nature, and dynamics of nationalist movements and ideologies, which have played a significant role in shaping modern politics, identity, and culture. While nationalism is a complex and multifaceted phenomenon, scholars have proposed various theories to understand its causes, manifestations, and consequences. In this discussion, we will enumerate some of the key theories of nationalism:
1. Primordialism:
Primordialism posits that nationalism is rooted in primordial, or innate, factors such as ethnicity, culture, language, and religion. According to this theory, nationalist sentiments emerge from deep-seated attachments to one’s ancestral homeland, kinship group, or cultural community, which are perceived as natural and immutable. Primordialists argue that nationalism is a natural expression of human sociality and identity, shaped by evolutionary, historical, and geographical factors. Scholars such as Clifford Geertz and Anthony D. Smith have explored the role of primordial ties and symbols in the formation of national identity and solidarity.
2. Modernism:
Modernism challenges the primordialist view by emphasizing the role of modernity, industrialization, and state-building in the emergence of nationalism. According to this theory, nationalism is a modern phenomenon that arises from the complex interactions between politics, economy, and culture in the context of nation-states. Modernists argue that nationalism is a product of specific historical conditions, such as the rise of capitalism, the decline of traditional social hierarchies, and the spread of mass education and communication. Scholars such as Ernest Gellner and Benedict Anderson have analyzed the role of nationalism in the construction of imagined communities and the homogenization of diverse populations into cohesive nation-states.
3. Ethnosymbolism:
Ethnosymbolism combines elements of primordialism and modernism by emphasizing the importance of symbols, rituals, and myths in the construction of national identity and solidarity. According to this theory, nationalism is based on shared cultural symbols and narratives that evoke a sense of collective belonging and continuity across time and space. Ethnosymbolists argue that national identity is not fixed or natural but is constructed and contested through ongoing processes of cultural representation and interpretation. Scholars such as Anthony D. Smith and John Armstrong have explored the role of ethnosymbols, such as flags, anthems, and monuments, in the formation and maintenance of national identity.
4. Instrumentalism:
Instrumentalism views nationalism as a strategic tool used by political elites to mobilize support, legitimize authority, and pursue specific political, economic, or social goals. According to this theory, nationalist movements and ideologies are often manipulated or instrumentalized by ruling elites to consolidate power, resist external threats, or mobilize popular support for regime legitimacy. Instrumentalists argue that nationalism is a contingent and flexible phenomenon that can be deployed for a variety of purposes, ranging from nation-building and state-building to ethnic mobilization and social control. Scholars such as Eric Hobsbawm and Ernest Gellner have analyzed the instrumental use of nationalism in different historical and political contexts.
5. Postcolonialism:
Postcolonialism examines nationalism in the context of colonialism, imperialism, and decolonization, focusing on the ways in which nationalist movements have sought to assert sovereignty, reclaim agency, and resist domination. According to this theory, nationalism emerges as a response to colonial oppression and cultural hegemony, as colonized peoples seek to reclaim their identity, autonomy, and dignity. Postcolonialists emphasize the role of anti-colonial struggles, cultural revitalization movements, and transnational solidarity networks in shaping nationalist discourses and practices. Scholars such as Frantz Fanon and Edward Said have analyzed the relationship between nationalism, imperialism, and liberation in the context of decolonization.
In summary, theories of nationalism offer diverse perspectives on the origins, nature, and dynamics of nationalist movements and ideologies. While primordialism emphasizes innate ties and identities, modernism focuses on historical and structural factors, ethnosymbolism highlights cultural symbols and narratives, instrumentalism underscores strategic uses of nationalism by political elites, and postcolonialism examines nationalism in the context of colonialism and decolonization. By exploring these theories, scholars seek to deepen our understanding of the complex and contested nature of nationalism in the modern world.

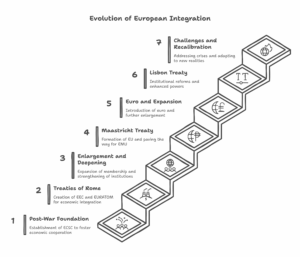
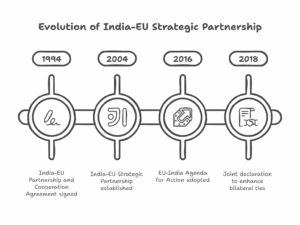
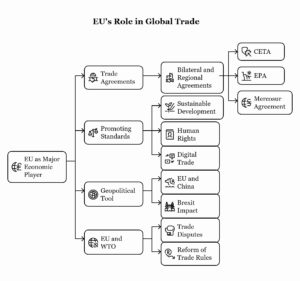
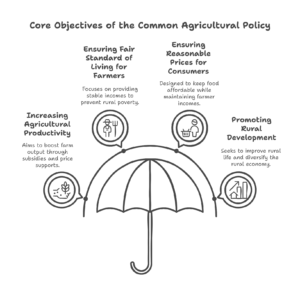
Leave a Reply