The pursuit of development and gender justice is a multifaceted endeavor that seeks to address disparities, inequalities, and discrimination based on gender while promoting inclusive and sustainable development. Critical examination of the relationship between development and gender justice reveals both progress and persistent challenges in achieving gender equality. Here’s an analysis of the development trajectory and the quest for gender justice:
Development and Gender Inequality:
1. Historical Context:
– Historically, development initiatives often overlooked gender disparities, focusing primarily on economic growth metrics without considering the differential impact on men and women. This approach perpetuated gender inequalities and marginalized women’s participation in the development process.
2. Economic Empowerment:
– Economic development has led to significant improvements in women’s access to education, employment, and income-generating opportunities. However, gender wage gaps, occupational segregation, and limited representation in decision-making positions persist, hindering women’s full economic empowerment.
3. Social Empowerment:
– Social development initiatives have aimed to address gender-based violence, discrimination, and harmful practices. Efforts to promote gender-sensitive education, healthcare, and social protection programs have contributed to enhancing women’s well-being and social inclusion. Yet, cultural norms, patriarchal attitudes, and structural barriers continue to impede progress in achieving gender justice.
Challenges and Opportunities:
1. Persistent Gender Gaps:
– Despite advancements, gender disparities persist across various dimensions, including education, health, political participation, and access to resources. Gender-based violence, unequal distribution of unpaid care work, and limited access to reproductive rights remain formidable challenges to gender equality.
2. Intersectionality:
– Intersectionality emphasizes the interconnected nature of social identities, such as gender, class, caste, ethnicity, and sexuality, and their impact on individuals’ experiences of oppression and privilege. Intersectional approaches to development recognize the intersecting forms of discrimination faced by marginalized women and advocate for inclusive policies and programs that address multiple dimensions of inequality.
3. Policy Interventions:
– Policy interventions, such as gender mainstreaming, affirmative action, and legal reforms, play a crucial role in advancing gender justice. Initiatives to promote women’s representation in decision-making bodies, ensure equal pay for equal work, and combat gender-based violence are essential steps towards achieving gender equality.
Conclusion:
The pursuit of development and gender justice requires a holistic and intersectional approach that addresses the root causes of gender inequality and empowers individuals of all genders to participate fully in society. While significant strides have been made in promoting gender equality, much remains to be done to dismantle patriarchal structures, challenge discriminatory norms, and create an enabling environment for women’s empowerment. Critical examination and sustained efforts to integrate gender perspectives into development policies, programs, and practices are essential for realizing the vision of a more just, equitable, and inclusive society.

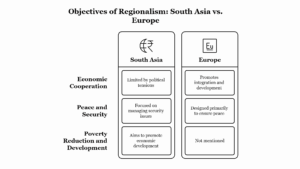
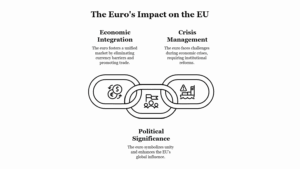
Leave a Reply