Liberal internationalism is a political ideology and foreign policy approach that advocates for international cooperation, the promotion of democracy, the rule of law, and the protection of human rights on a global scale. Rooted in the liberal tradition, this ideology emphasizes the potential for progress in international relations through diplomacy, institutions, and norms that promote…
Category: Uncategorized
Nature of relationships among Executive, Legislature, and Judiciary in Canada
Canada’s system of governance is based on the principles of a constitutional monarchy and a parliamentary democracy. This system functions within the framework of the British North America Act of 1867, which laid down the federal structure, and the Constitution Act of 1982, which formally recognized the rights and freedoms of Canadian citizens. The relationships…
Role of Pressure Groups in Canadian Politics
Pressure groups, often referred to as interest groups or lobby groups, play a crucial role in the political landscape of Canada. These organizations seek to influence public policy, decision-making, and legislation in favor of specific interests, ideas, or causes. Pressure groups are not political parties, as they do not contest elections, but they can exert…
Canada’s economic relationship with the European Union
Canada’s economic relationship with the European Union (EU) is robust and multifaceted, shaped by trade, investment, political ties, and shared interests on global issues. Over the years, this relationship has evolved from a focus on trade agreements and diplomatic ties to one that includes deeper economic integration, cultural exchange, and collaboration on global challenges. The…
Political forces have worked towards reducing the centre’s grip over the states
The relationship between the central government and state governments in India has been a subject of constant tension and negotiation, especially in the post-independence period. While the Indian Constitution established a federal structure, the central government has often been accused of consolidating power at the center, limiting the autonomy of the states. However, over the…
Analyse the basic objectives of European Union’s development policy.
The European Union’s development policy plays a crucial role in the EU’s external relations and its commitment to global peace, security, and sustainable development. The policy aims to contribute to reducing poverty, promoting sustainable development, and fostering global peace through cooperation with developing countries. Over the years, the EU has shaped its development policy to…
The Marxian approach to study state politics
The Marxian approach to studying state politics is rooted in the philosophy of historical materialism, which suggests that the structure of society is primarily determined by its economic base. According to Karl Marx, the state is not a neutral or impartial entity but rather a tool that serves the interests of the ruling economic class….
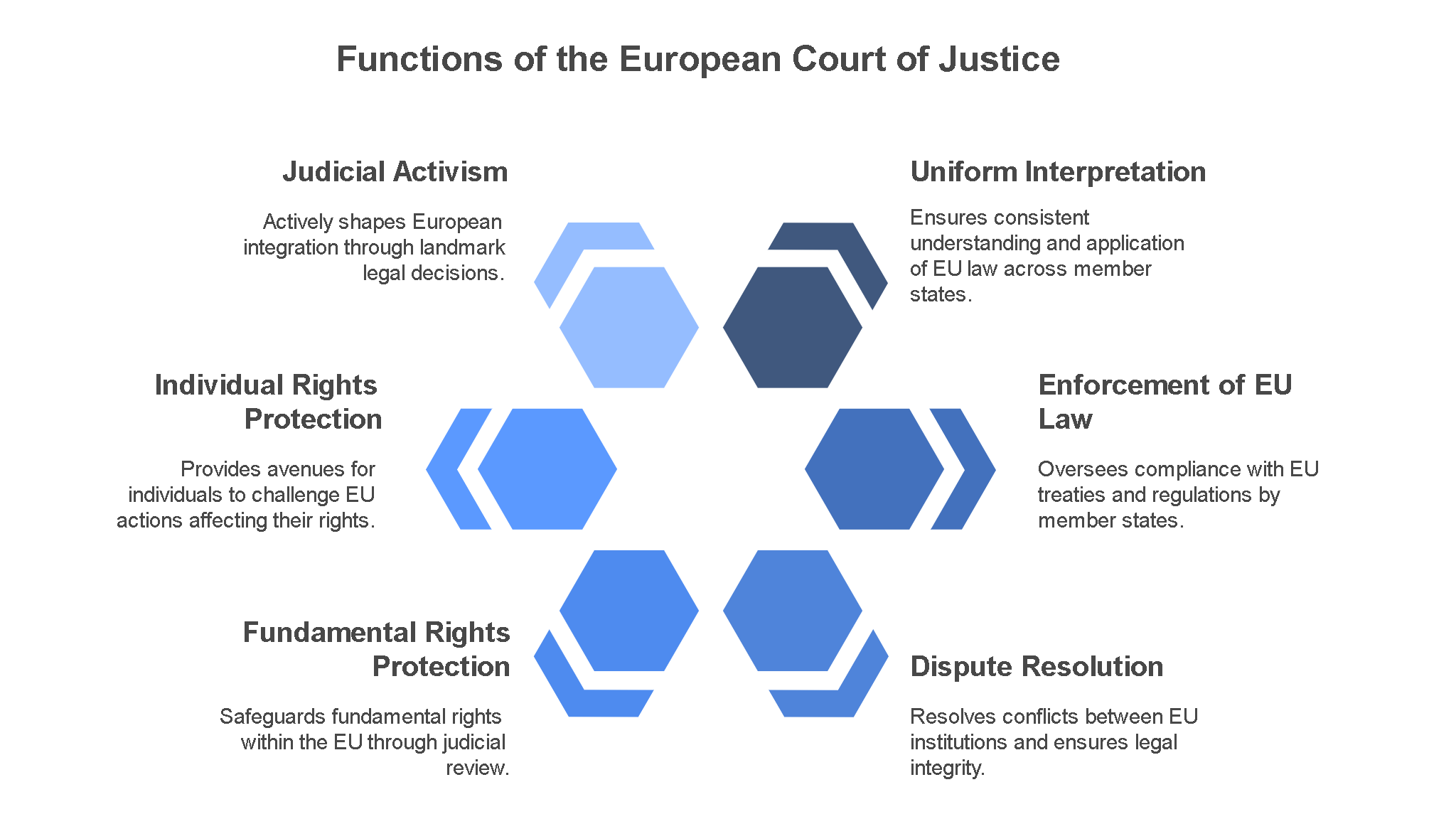
Functions of the European Court of Justice
The European Court of Justice (ECJ), established in 1952, is the highest judicial authority within the European Union (EU). It is located in Luxembourg and plays a central role in ensuring the uniform application and interpretation of EU law across all member states. The ECJ is tasked with upholding the legal order of the European…
European-Union and SAARC
The European Union (EU) and the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) represent two distinct regional organizations: the EU is a political and economic union primarily composed of European countries, while SAARC is a regional organization comprising countries from South Asia. Despite their different structures, these organizations engage in various forms of cooperation, both…
Briefly describe the systemic and post-modernist frameworks to analyse State politics in India
In the study of state politics in India, two significant theoretical frameworks are the systemic and post-modernist approaches. Both offer distinct perspectives on how the state operates, the nature of political power, and the dynamics of governance in India. These frameworks help scholars and analysts understand the political landscape of India, where federalism, social hierarchies,…
Explain the meaning and importance of social movements
Meaning of Social Movements: A social movement is a collective, organized, and sustained effort by a large group of people to promote or resist social change. According to sociologist Charles Tilly, social movements are “a series of contentious performances, displays, and campaigns by which ordinary people make collective claims on others.” These movements typically arise…
Critically analyse the characteristics of the new social movements
New social movements (NSMs) are a type of collective action that emerged in the latter half of the 20th century, primarily in the developed world but also influencing global social dynamics. These movements differ significantly from traditional social movements in both form and content. They focus not only on economic and political demands but also…